Creating a balanced diet is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. A balanced diet provides your body with the necessary nutrients to function optimally, supports healthy weight management, and helps prevent chronic diseases. Here’s a detailed guide on how to create a balanced diet that meets your nutritional needs and promotes optimal health:
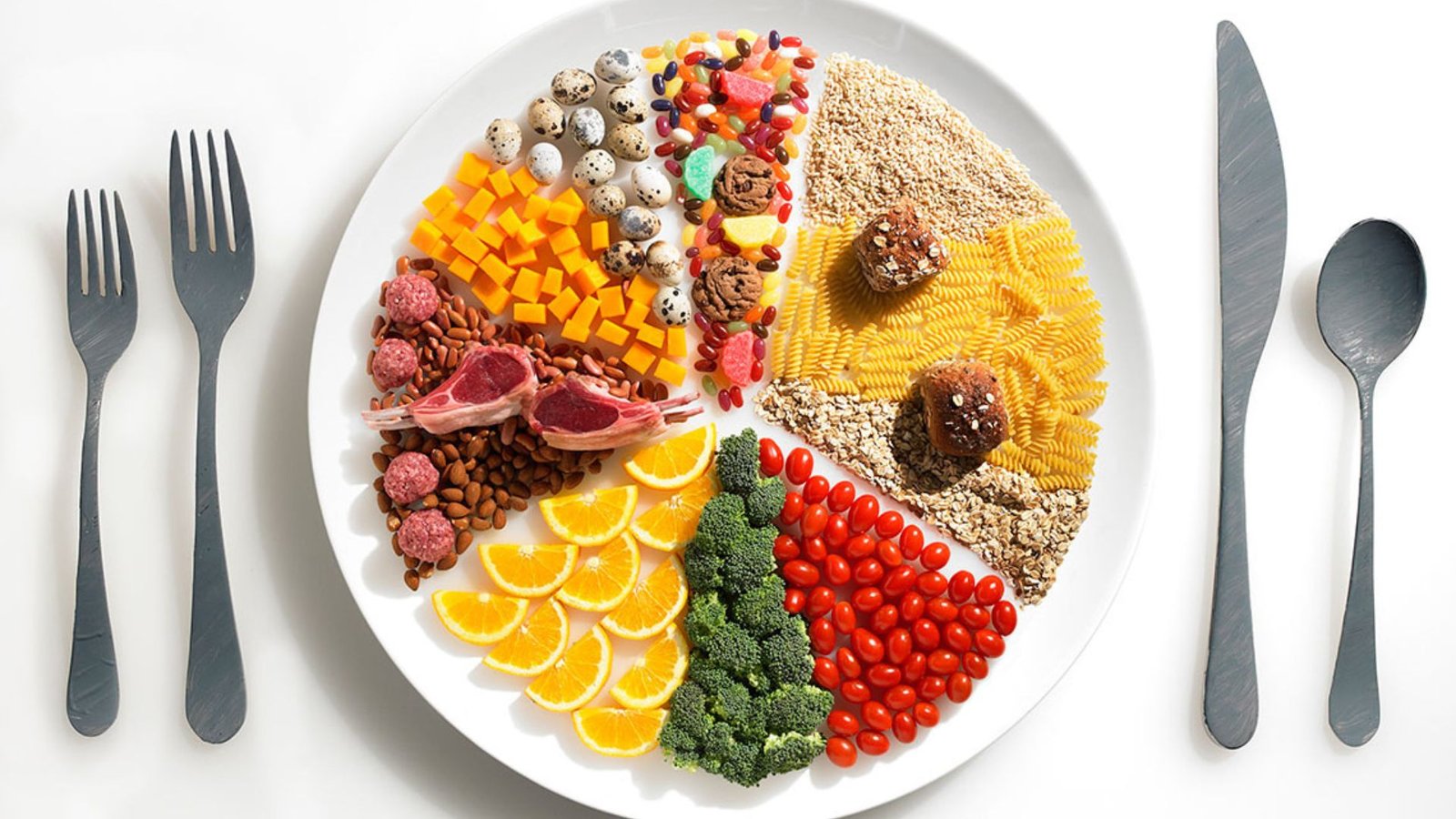

Understand the Basics of a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet includes a variety of foods in the right proportions to provide essential nutrients. The key components of a balanced diet are:
- Macronutrients: These include carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each macronutrient plays a vital role in providing energy and supporting bodily functions.
- Micronutrients: Vitamins and minerals are crucial for various bodily functions, including immune support, bone health, and energy production.
- Water: Staying hydrated is essential for overall health and supports many bodily functions.
Incorporate a Variety of Foods
To achieve a balanced diet, incorporate a wide range of foods from different food groups:
- Fruits and Vegetables: Aim to fill half your plate with fruits and vegetables. They are rich in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and fiber. Choose a variety of colors to ensure you get a broad spectrum of nutrients.
- Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains such as brown rice, quinoa, oats, and whole wheat products. Whole grains provide fiber, B vitamins, and essential minerals.
- Lean Proteins: Include sources of lean protein such as poultry, fish, beans, lentils, tofu, and low-fat dairy. Protein is essential for muscle repair, immune function, and overall growth.
- Healthy Fats: Choose sources of healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. Healthy fats support brain health, hormone production, and cell function.
Portion Control
Portion control helps manage calorie intake and maintain a healthy weight. Use the following strategies to control portions:
- Use Smaller Plates: Smaller plates can help control portion sizes and prevent overeating.
- Pay Attention to Hunger Cues: Eat when you are hungry and stop when you are satisfied, not full.
- Read Nutrition Labels: Nutrition labels provide information on serving sizes and help you make informed choices about portion sizes.
Balance Macronutrients
A balanced diet includes appropriate proportions of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats:
- Carbohydrates: They should make up about 45-65% of your total daily calories. Focus on complex carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables rather than refined sugars and processed foods.
- Proteins: Aim for 10-35% of your daily calories from protein sources. Include a mix of animal and plant-based proteins.
- Fats: Fats should constitute 20-35% of your daily calories. Emphasize unsaturated fats and limit saturated and trans fats.
Stay Hydrated
Water is a crucial part of a balanced diet. Aim to drink at least 8 cups (64 ounces) of water daily. Adjust your intake based on factors such as physical activity, climate, and individual needs.
Limit Added Sugars and Salt
Excessive consumption of added sugars and salt can contribute to health problems such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and diabetes. To limit intake:
- Read Labels: Check for added sugars and sodium in packaged foods.
- Cook at Home: Preparing meals at home allows you to control the amount of salt and sugar in your diet.
- Choose Natural Sweeteners: Opt for natural sweeteners like honey or fruit instead of processed sugars.
Plan Your Meals
Meal planning helps ensure you have a variety of nutritious foods and can prevent unhealthy eating habits. Consider the following:
- Prepare Balanced Meals: Include a mix of proteins, grains, vegetables, and healthy fats in each meal.
- Snack Wisely: Choose healthy snacks like fruits, nuts, and yogurt to maintain energy levels between meals.
- Stay Organized: Create a weekly meal plan and grocery list to help you stay on track with your balanced diet.
Listen to Your Body
Everyone’s nutritional needs are different. Pay attention to how different foods make you feel and adjust your diet accordingly. Consult with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian for personalized advice based on your health goals and conditions.
Conclusion
Creating a balanced diet involves incorporating a variety of nutrient-dense foods, controlling portion sizes, and maintaining proper hydration. By focusing on a mix of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, you can support optimal health and well-being. Remember to plan your meals, listen to your body’s needs, and seek professional guidance for personalized dietary recommendations.